Pseudoarthrosis
Pseudoarthrosis, how and when it arises.
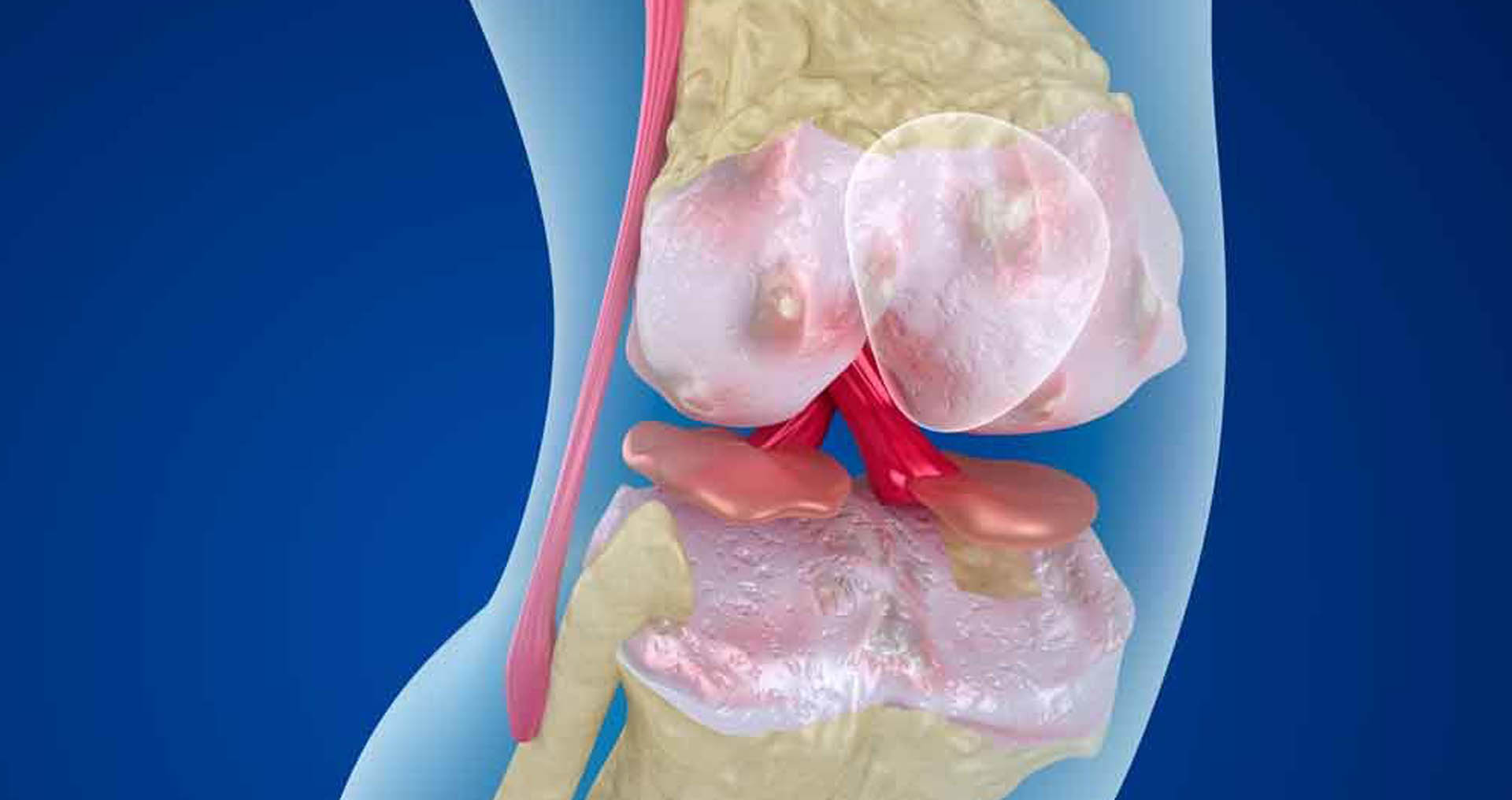
When a fracture fails to calcify correctly, even if subjected to the most common modern therapeutic methods, it is pseudoarthrosis. In such a condition the human body fails in the process of bone callus formation, due to advanced age, metabolic disorders, alcohol intake and smoking, infection or lack of vascularization.
What are the symptoms?
The most common symptoms are certainly pain, crunching and the feeling that the bones are not stable and therefore moving.
Diagnosis
When the pain persists for more than six months after the fracture and fails to calcify in biological times, the orthopedist is able to confirm the pseudoarthrosis by radiographic or more special examinations such as CT scan or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Indicated treatments
Therapeutic methods can be different:
- The grafting of a portion of the patient’s bone directly into the area of the lesion.
- Insertion of synthetic means such as metal plates, screws, pins that are screwed inside the bone to stabilize the fragments.
- Regenerative magnetotherapy applications that stimulate the proliferation of osteoblasts (active bone tissue cells) in order to consolidate the formation of bone callus.
Osteoplus® magnetotherapy is particularly effective in regenerating bone tissue through a specific and focused treatment